机器学习分析影响体重的生活因素
之前本科的毕设是做的数据挖掘的关联分析,前两天看到有人用机器学习来做分析生活习惯的,觉得也挺有意思的,拿起课本玩了一下,结果令人感叹。
以下是截图:
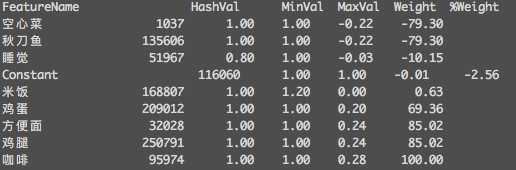
数据不太多,还不够准确,利用VW框架回归确实方便。还需要多记录下日常。
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# vim: ts=4 sw=4 expandtab
"""
vw-varinfo2: vw dataset summary & variable importance
This is new & simpler implementation of the original vw-varinfo
It is designed to be simpler and faster. There's less dependence
on command line options so it is much more robust against future
changes and new options in vowpal-wabbit.
This implementation is in python (original was in perl)
TODO: multi-class support is not implemented!
Author: Ariel Faigon (2016)
"""
import sys
import os
import subprocess
import re
import argparse
import string
import itertools
import tempfile
Verbose = False
ARGV0 = os.path.basename(sys.argv[0])
# Default vw executable program to call
VW = 'vw'
# Additional VW args which should be reused from 1st to 2nd pass
VWARGS = []
# Hash mappings for per-feature (min, max, hash-value, weight)
F_MIN = {}
F_MAX = {}
F_HASH = {}
F_WEIGHT = {}
# We need to have a model at the end to load all weights
# If it is not supplied on the command line, we add it ourselves
ModelName = ''
CleanupModel = False
# A global switch and list of all seen labels to support MultiClass
MultiClass = False
MCLabels = None
def v(msg):
"""print message to stderr"""
sys.stderr.write("%s\n" % msg)
sys.stderr.flush()
def d(msg):
"""Verbose/debugging message, activated with '-v' option."""
if not Verbose:
return
v(msg)
def fatal(msg):
"""fatal (can't continue) situation error message"""
v("== FATAL: %s" % msg)
sys.exit(1)
def usage(msg):
"""Print usage message and exit"""
if msg:
v(msg)
v("Usage: %s [-v] [<vw>] <vw_args>..." % ARGV0)
v(" Notes:\n"
"\tYou may omit the <vw> argument (default is 'vw')\n"
"\tYou may use a different <vw> executable as the 1st arg\n"
"\t<vw_args> are all the vw arguments, as you would call vw directly\n"
"\tIf <vw_args> is just a dataset-file - vw defaults will be used"
)
sys.exit(1)
def which(program):
"""
Find a program in $PATH
If found, return its full path, otherwise return None
"""
def is_exe(fpath):
return os.path.isfile(fpath) and os.access(fpath, os.X_OK)
fpath, fname = os.path.split(program)
if fpath:
if is_exe(program):
return program
else:
for path in os.environ["PATH"].split(os.pathsep):
path = path.strip('"')
exe_file = os.path.join(path, program)
if is_exe(exe_file):
return exe_file
return None
def all_features_dicts():
"""
Returns two dict of all features in a structured way:
1st dict is individual features: scalar keys with a value of 1
2nd dict is for features within name-spaces, key is the name-space
first dict is:
{
# individual (not in a name-space) features:
"f1": 1,
"f2": 1,
"fN": 1
}
second dict is:
{
# features in name-spaces:
"namespace1": { "f1":1, "f2":1, ... },
"namespace2": {"f1":1, "f2":1, ... },
}
"""
d1 = {}
d2 = {}
for k in F_HASH:
if '^' in k:
ns, fname = k.split('^', 1)
if not ns in d2:
d2[ns] = {}
d2[ns][fname] = 1
else:
# Constant feature should never be added as a regular
# feature. vw adds it by itself as needed.
# TODO: multiclass uses separate Constant_<N> per class
if k != 'Constant':
d1[k] = 1
return d1, d2
def all_features_example():
"""Return a equal-weight vw line with all features present"""
# TODO: implement multi-class: needs per-class internal data-structs
d1, d2 = all_features_dicts()
individual_features = ' | ' + ' '.join(d1.keys())
ns_features = []
for ns in d2:
fnames = d2[ns].keys()
one_ns_features = " |%s %s" % (ns, ' '.join(fnames))
ns_features.append(one_ns_features)
example = '1' + individual_features + ' '.join(ns_features) + '\n'
d("all_features_example: %s" % example)
return example
def process_audit_line(line):
features = line.split("\t");
features.pop(0)
for f in features:
fields = f.split(':')
fname = fields[0]
fhash = int(fields[1])
fval = float(fields[2])
fweight = float(fields[-1].split('@')[0])
F_WEIGHT[fname] = fweight
F_HASH[fname] = fhash
if not fname in F_MIN:
# feature seen for 1st time
F_MIN[fname] = fval
F_MAX[fname] = fval
if fval < F_MIN[fname]:
F_MIN[fname] = fval
if fval > F_MAX[fname]:
F_MAX[fname] = fval
def vw_audit(vw_cmd, our_input=None):
"""
Generator for vw audit-lines
(Each example is mapped to its audit-line)
vw_cmdline is a list of args to run vw with
There are two modes of running:
1) Normal: input provided directly to vw from command line
2) 2nd pass: input provided by vw-varinfo as a string
This mode is activated when our_input="some string..."
"""
if our_input:
# Input comes from our_input (string)
# which is sent to stdin of the subprocess
vw_proc = subprocess.Popen(
vw_cmd,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
stdin=subprocess.PIPE,
bufsize=1048576
)
vw_proc.stdin.write(our_input)
vw_proc.stdin.close()
else:
# By default, vw reads from a training-set
# which is already provided on the command line
vw_proc = subprocess.Popen(
vw_cmd,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
close_fds=False,
bufsize=1048576
)
re_leading_tab = re.compile(r'^\t')
example_no = 0
while True:
vw_line = vw_proc.stdout.readline()
if vw_line == '':
# End of input
vw_proc.stdout.close()
vw_proc.wait()
if vw_proc.returncode:
fatal("vw subprocess failed (status=%s): '%s'" %
(vw_proc.returncode, vw_cmd)
)
else:
d("%s: %s examples, exit status: %s" %
(vw_cmd, example_no, vw_proc.returncode)
)
return
if re_leading_tab.match(vw_line):
# An audit line (what we're looking for)
example_no += 1
d(vw_line)
yield vw_line
continue
# anything we want to do with other lines?
def run_vw(vw_cmd, our_input=None):
audit_lines = vw_audit(vw_cmd, our_input)
for line in audit_lines:
process_audit_line(line)
def is_vw_arg(arg):
"""
Return True iff the arg looks like a 'vw' argument
Side effect: modifies the VW global variable iff user uses
a different vw
"""
global VW
if arg == VW:
return True
if re.search(r'(?:^|/)vw[-_.0-9]*$', arg):
VW = arg
return True
return False
def already_has_audit(args):
"""Return True iff args already include --audit (or -a)"""
if '-a' in args or '--audit' in args:
return True
return False
def is_multiclass(args):
"""
Check args for any hint of a multiclass problem
(Check is option dependent and may be incomplete)
"""
# Not sure if --wap, --ect multi-class are actually right
for mc_opt in ('--oaa', '--csoaa', '--ect', '--wap', '--sequence'):
if mc_opt in args:
return True
return False
def model_arg(args):
"""Return the model arg if any"""
f_idx = None
try:
f_idx = args.index('-f')
except:
# not there
return None
try:
f_idx += 1
model = args[f_idx]
except:
fatal("Oops! -f withot an arg - can't continue")
return model
def get_vw_cmd(args):
"""
Return the vw command we want to run
This means stripping our own (vw-varinfo) name from the list
and making sure:
1) That we have 'vw' at the beginning
2) That -a is added for auditing
"""
global ModelName, CleanupModel, VWARGS, Verbose
if len(args) <= 1:
usage('')
# -- move ourselves (vw-varinfo arg) out of the way
args.pop(0)
# 1st arg can be '-v' for debugging this script
if len(args) > 0 and args[0] == '-v':
Verbose = True
args.pop(0)
vw_args = []
if len(args) < 1:
usage('Too few args: %s' % args)
if not is_vw_arg(args[0]):
args.insert(0, 'vw')
if not already_has_audit(args):
args.insert(1, '--audit')
if '--noconstant' in args:
VWARGS.append('--noconstant')
model = model_arg(args)
if model:
ModelName = model
else:
ModelName = tempfile.mktemp(suffix='.vwmodel')
args.insert(1, ModelName)
args.insert(1, '-f')
CleanupModel = True
# TODO: skip leading options that are intended for vw-varinfo itself
for arg in args:
vw_args.append(arg);
d("vw_cmd is: %s" % vw_args)
vw_exe = vw_args[0]
if which(vw_exe) == None:
fatal("Sorry: can't find %s (vowpal wabbit executable) in $PATH\n"
"PATH=%s" % (vw_exe, os.environ["PATH"]))
return vw_args
def minmax(data):
"""
Return a pair (min, max) of list arg
Credit: https://code.activestate.com/recipes/577916-fast-minmax-function/
Computes the minimum and maximum values in one-pass using only 1.5*len(data) comparisons
"""
it = iter(data)
try:
lo = hi = next(it)
except StopIteration:
raise ValueError('minmax() arg is an empty sequence')
for x, y in itertools.izip_longest(it, it, fillvalue=lo):
if x > y:
x, y = y, x
if x < lo:
lo = x
if y > hi:
hi = y
return lo, hi
def fix_weights_pass2():
"""
Run a 2nd pass with all features and stored model
To get the final weights for all features
"""
global Model
vw_cmd = [VW, '--quiet', '-t', '-a', '-i', ModelName]
if len(VWARGS) > 0:
vw_cmd += VWARGS
run_vw(vw_cmd, all_features_example())
def summarize():
"""Output summary of variables"""
wmin, wmax = minmax(F_WEIGHT.values())
w_absmax = max(abs(wmin), abs(wmax))
# Print a header
print("%-16s\t%10s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" %
('FeatureName', 'HashVal', 'MinVal', 'MaxVal', 'Weight', '%Weight'))
# TODO: implement multi-class
# multi-class needs per-class internal data-structs
# To reverse-order add: 'reverse=True' arg to 'sorted'
sorted_tuples = sorted(F_WEIGHT.items(), key=lambda(k,v): v)
for fname, fval in sorted_tuples:
fmin = float(F_MIN[fname])
fmax = float(F_MAX[fname])
fweight = float(F_WEIGHT[fname])
fhash = F_HASH[fname]
relscore = 100.0 * (fweight/w_absmax if w_absmax > 0 else 0.0)
print("%-16s\t%10s\t%.2f\t%.2f\t%.2f\t%7.2f" %
(fname, fhash, fmin, fmax, fweight, relscore))
#
# -- main
#
def main():
"""Main func for vw-varinfo2: dataset feature information summary"""
global MultiClass, MCLabels
vw_cmd = get_vw_cmd(sys.argv)
if is_multiclass(vw_cmd):
# multi-class needs per-class internal data-structs
MultiClass = True
MCLabels = []
run_vw(vw_cmd)
# Run second pass:
# with -i ModelName and single example w/ all-features present
fix_weights_pass2()
summarize()
if CleanupModel:
d("removing tempfile: %s" % ModelName)
os.remove(ModelName)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()

This work is licensed under a CC A-S 4.0 International License.